How to operate a drone safely and effectively is a skill that opens up a world of exciting possibilities, from breathtaking aerial photography to efficient surveying. This guide provides a structured approach, covering everything from understanding your drone’s components to mastering advanced flight techniques and adhering to crucial safety regulations. We’ll explore pre-flight checks, essential maneuvers, camera operation, battery management, troubleshooting, and legal considerations, ensuring you’re well-prepared for a successful and responsible drone piloting experience.
Whether you’re a complete beginner or looking to refine your existing skills, this comprehensive guide will equip you with the knowledge and confidence to take to the skies responsibly. We’ll break down complex concepts into easy-to-understand steps, illustrated with helpful diagrams and practical examples. By the end, you’ll be ready to embark on your aerial adventures with confidence and skill.
Drone Components and Terminology
Understanding the various components of a drone and their functions is crucial for safe and effective operation. This section details the key parts of a typical drone, along with a glossary of common terms.
Major Drone Components and Their Functions
A drone comprises several interconnected systems working in harmony. Here’s a breakdown of the key components:
- Propellers: These rotating blades generate thrust, enabling the drone to take off, fly, and land. Different propeller designs offer varying levels of thrust and efficiency.
- Motors: Electric motors power the propellers. Their speed and direction are controlled by the flight controller.
- Flight Controller: The “brain” of the drone, this onboard computer processes data from various sensors (gyroscopes, accelerometers, GPS) and controls the motors to maintain stability and execute flight commands.
- Battery: Provides the power source for the drone’s motors, flight controller, and camera. Battery life is a critical factor affecting flight time.
- Camera: Captures photos and videos. Different drones offer varying camera resolutions, features, and image stabilization capabilities.
- Transmitter (Remote Controller): Allows the pilot to control the drone’s movements and camera functions wirelessly.
Drone Terminology Glossary
Familiarizing yourself with common drone terminology is essential. Here’s a glossary of frequently used terms and acronyms:
- ESC (Electronic Speed Controller): Regulates the power supplied to each motor.
- GPS (Global Positioning System): Enables the drone to determine its location and maintain position.
- IMU (Inertial Measurement Unit): Measures the drone’s orientation and movement using accelerometers and gyroscopes.
- RTF (Ready-To-Fly): A drone that comes fully assembled and ready to fly out of the box.
- FPV (First-Person View): A system that allows the pilot to see what the drone’s camera sees in real-time.
- LiPo (Lithium Polymer): A common type of rechargeable battery used in drones.
- Gimbal: A stabilized mount for the camera, reducing vibrations and improving image quality.
- Payload: The weight carried by the drone, including the camera and other equipment.
Drone Propeller Comparison
Different propellers are optimized for various flight characteristics and drone types. The following table provides a comparison of common propeller types:
| Material | Size (Diameter) | Pitch | Characteristics |
|---|---|---|---|
| Plastic | 5 inch | 3 inch | Lightweight, affordable, suitable for beginners |
| Carbon Fiber | 8 inch | 5 inch | Strong, durable, higher performance |
| Nylon | 7 inch | 4 inch | Good balance of strength and flexibility |
| Plastic | 6 inch | 2 inch | Good for slow and precise movements |
Pre-Flight Checklist and Safety Procedures

A thorough pre-flight checklist and adherence to safety procedures are paramount for preventing accidents and ensuring safe drone operation.
Pre-Flight Checklist
Before each flight, follow this comprehensive checklist:
- Inspect the drone for any visible damage to propellers, motors, or body.
- Check the battery level and ensure it’s fully charged.
- Verify GPS signal acquisition. The drone should have a solid GPS lock before takeoff.
- Calibrate the compass and IMU if necessary.
- Check the transmitter batteries and ensure a strong connection with the drone.
- Review the weather conditions and avoid flying in strong winds or rain.
- Confirm you’re in a permitted airspace and not violating any regulations.
Safe Drone Operation Practices
Safe drone operation involves more than just a pre-flight checklist. It requires adherence to airspace regulations, understanding emergency procedures, and maintaining situational awareness.
- Always maintain visual line of sight (VLOS) with your drone.
- Avoid flying near airports, airfields, or other restricted airspace.
- Never fly over crowds or people.
- Be aware of the surrounding environment and avoid obstacles.
- Know and follow all local drone regulations and laws.
- Have a plan for emergency situations, such as loss of signal or battery failure.
Safe Pre-Flight Routine Flowchart
A visual representation of a safe pre-flight routine can help ensure all steps are followed consistently.
(A detailed flowchart would be included here, depicting the steps Artikeld in the pre-flight checklist, progressing from inspection to final checks before takeoff. The flowchart would use standard flowchart symbols like rectangles for processes, diamonds for decisions, and arrows to indicate flow.)
Taking Off and Landing
Proper takeoff and landing techniques are essential for safe and efficient drone operation, varying based on environmental conditions.
Takeoff and Landing Techniques
The process involves a series of steps to ensure a smooth and controlled ascent and descent.
- Assisted Takeoff: Many drones offer assisted takeoff modes that automatically handle the initial ascent, simplifying the process for beginners.
- Manual Takeoff: Requires more skill and involves gently increasing throttle to lift the drone vertically.
- Landing: Gradually reduce throttle to descend smoothly. Always maintain control and prepare for a potential unexpected landing.
In windy conditions, a more controlled and gradual approach is necessary. Consider using a sheltered area or adjusting your flight plan to account for wind gusts.
Obstacle Avoidance During Takeoff and Landing
Maintaining awareness of your surroundings is critical. Clear the area of any potential obstacles before takeoff and landing. Use the drone’s camera and sensors to assess the environment.
Drone Flight Controls and Maneuvers
Understanding drone flight controls is fundamental to safe and effective operation. This section explains the function of each control stick and provides instructions for basic maneuvers.
Drone Transmitter Control Sticks
Standard drone transmitters typically have two control sticks:
- Left Stick: Controls altitude (vertical movement) and yaw (rotation around the vertical axis).
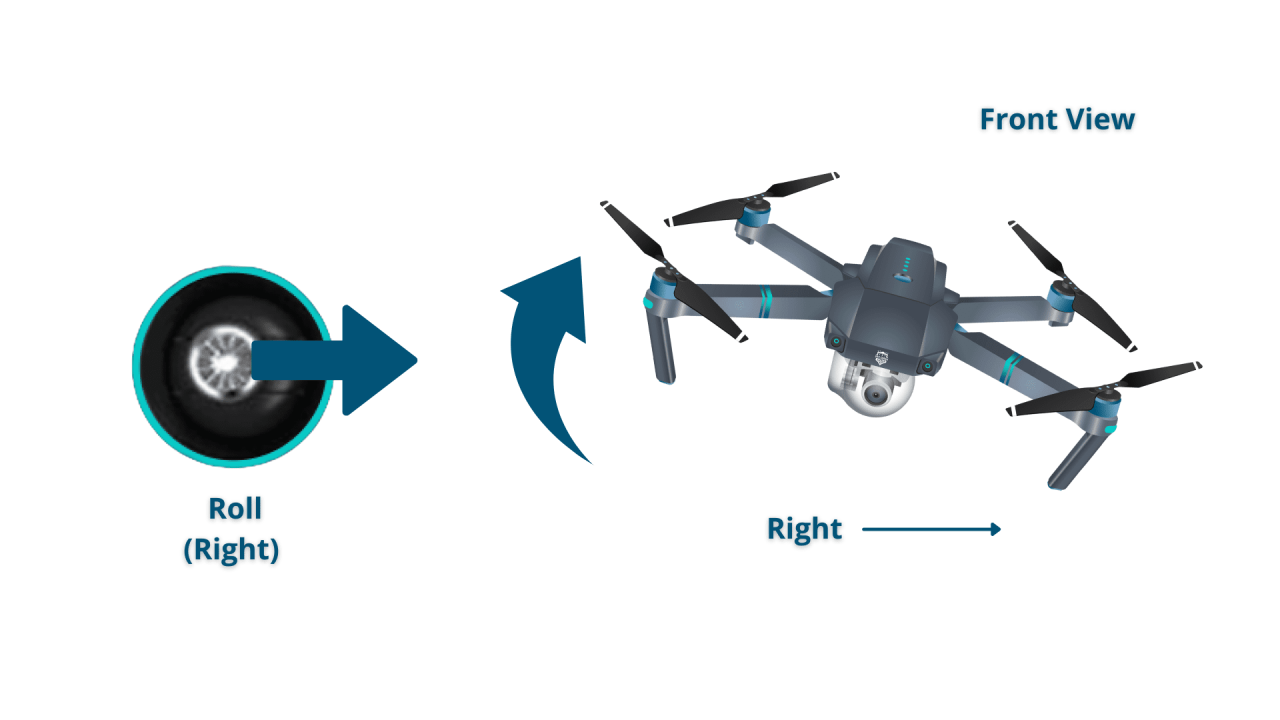
- Right Stick: Controls pitch (forward/backward movement) and roll (left/right movement).
Basic Flight Maneuvers
Mastering these maneuvers is essential for confident drone operation:
- Hovering: Maintaining a steady position in the air.
- Ascending: Moving upwards.
- Descending: Moving downwards.
- Yawing: Rotating the drone left or right.
- Pitching: Moving the drone forward or backward.
- Rolling: Moving the drone left or right sideways.
Common Flight Errors and Solutions
Pilots frequently encounter certain issues. Here are some common errors and their solutions:
- Loss of signal: Check transmitter batteries, ensure clear line of sight, and fly within the drone’s range.
- Drone drifting: Calibrate the compass and IMU, ensure GPS signal is strong.
- Sudden descent: Check battery level, ensure propellers are undamaged.
- Unresponsive controls: Check transmitter batteries and connection, reboot the drone.
Drone Camera Operation and Image Capture
Many drones are equipped with high-quality cameras, offering various modes and settings to capture stunning aerial footage. Understanding camera operation and settings is key to producing high-quality results.
Drone Camera Modes
Most drones offer several camera modes:
- Photo Mode: Captures still images.
- Video Mode: Records video footage.
- Timelapse Mode: Captures a series of photos at set intervals, which can be combined into a time-lapse video.
Optimizing Image Quality
Several settings influence image quality:
- Resolution: Higher resolution means larger image files but better detail.
- ISO: Controls the sensitivity to light; lower ISO for brighter conditions, higher ISO for low-light.
- Shutter Speed: Affects motion blur; faster shutter speeds freeze motion, slower speeds create motion blur.
- Aperture: Controls the depth of field; wider apertures create shallow depth of field (blurred background), narrower apertures create greater depth of field (everything in focus).
Tips for High-Quality Aerial Photos and Videos
To achieve professional-looking results, consider these tips:
- Fly in good lighting conditions.
- Use a gimbal for smooth video footage.
- Experiment with different angles and perspectives.
- Plan your shots in advance.
- Edit your photos and videos post-flight.
Battery Management and Charging
Proper battery care is crucial for maximizing flight time and ensuring the longevity of your drone’s battery. This section details safe charging and storage practices.
Importance of Proper Battery Care
LiPo batteries require careful handling to prevent damage and ensure safety. Overcharging, discharging too deeply, or improper storage can lead to battery failure or even fire.
Safe Charging and Storage
Always charge LiPo batteries using a dedicated LiPo charger and follow the manufacturer’s instructions. Store batteries in a cool, dry place, away from flammable materials.
Comparison of Drone Battery Types
LiPo and LiHV (Lithium Polymer High Voltage) batteries are commonly used in drones. LiHV batteries offer higher voltage and energy density than LiPo batteries, resulting in longer flight times but also requiring specific chargers.
| Battery Type | Voltage | Energy Density | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| LiPo | 3.7V per cell | Moderate | Widely available, relatively inexpensive | Shorter flight times compared to LiHV |
| LiHV | 4.35V per cell | Higher | Longer flight times | Requires specific chargers, potentially more expensive |
Troubleshooting Common Drone Issues
Even with careful operation, drone malfunctions can occur. This section identifies common problems and provides troubleshooting steps.
Common Drone Malfunctions and Troubleshooting, How to operate a drone
Here are some frequent issues and how to address them:
- Loss of Signal: Check transmitter batteries, obstructions, and distance from the drone. Ensure a clear line of sight.
- Motor Failure: Inspect propellers and motors for damage. Check motor connections and ESC functionality.
- GPS Issues: Ensure sufficient satellites are acquired. Try recalibrating the GPS and compass.
- Battery Problems: Check battery voltage and condition. Ensure proper charging procedures are followed.
Common Error Codes and Meanings
Many drones display error codes to indicate specific problems. Consult your drone’s manual for a complete list of error codes and their meanings.
| Error Code | Meaning | Solution |
|---|---|---|
| Error 1 | Low Battery | Charge the battery |
| Error 2 | GPS Signal Lost | Move to an open area with a clear view of the sky |
| Error 3 | Motor Malfunction | Inspect motors and propellers for damage |
| Error 4 | Overheating | Allow the drone to cool down before restarting |
Drone Laws and Regulations
Operating a drone responsibly involves understanding and adhering to all relevant laws and regulations. This section discusses legal considerations for drone operation.
Drone Laws and Regulations in Your Region
Drone laws vary significantly by location. It is crucial to research and understand the specific regulations in your area before flying. This typically includes registration requirements, airspace restrictions, and operational limitations.
Obtaining Necessary Permits and Licenses
Depending on your location and intended use, you may need to obtain permits or licenses to operate a drone legally. These permits may be required for commercial use, flying in specific airspace, or operating certain types of drones.
Consequences of Violating Drone Regulations
Violating drone regulations can lead to serious consequences, including fines, drone confiscation, and even criminal charges. Understanding and complying with all applicable laws is essential for responsible drone operation.
Advanced Drone Techniques
Beyond basic flight maneuvers, drones offer advanced capabilities that enhance their versatility and utility. This section explores advanced flight techniques and software applications.
Advanced Flight Maneuvers
Advanced techniques expand the possibilities of drone operation:
- Waypoint Navigation: Pre-programming a flight path for the drone to follow autonomously.
- Automated Flight Modes: Utilizing features like “Follow Me” or “Orbit” modes for creative shots.
- Precision Landing: Utilizing GPS and visual sensors for precise landing in designated locations.
Drone Software for Flight Planning and Mission Control
Specialized software enhances flight planning and mission execution. These applications allow users to plan complex flight paths, set waypoints, and control various drone functions remotely.
Creative Aerial Photography and Videography Techniques
Advanced techniques unlock creative potential:
- Drone Cinematography: Using smooth camera movements and creative angles to enhance video storytelling.
- Aerial Panoramas: Stitching together multiple photos to create wide-angle panoramic images.
- Time-lapse Photography: Capturing the movement of clouds, traffic, or other time-based phenomena.
Drone Maintenance and Cleaning: How To Operate A Drone
Regular maintenance and cleaning are essential for preserving the performance and longevity of your drone. This section provides a guide for maintaining your drone.
Drone Cleaning and Maintenance Procedures

Cleaning your drone regularly prevents the accumulation of dirt and debris that can affect performance and stability. Inspect the drone for damage after each flight.
- Clean the drone body with a soft cloth and mild soap.
- Inspect propellers, motors, and other components for any damage or wear.
- Check all screws and connections to ensure they are secure.
- Clean the camera lens with a lens cleaning cloth.
Inspecting for Damage and Performing Minor Repairs
Regular inspection helps identify potential issues before they become major problems. Minor repairs, such as replacing damaged propellers, can often be performed at home.
Routine Drone Maintenance Schedule
Establish a regular maintenance schedule to ensure your drone remains in optimal condition.
| Maintenance Task | Frequency |
|---|---|
| Visual inspection | After each flight |
| Cleaning | Weekly or as needed |
| Calibration | Monthly or as needed |
| Battery maintenance | As needed |
Mastering the art of drone operation involves a blend of technical understanding, practical skills, and a strong commitment to safety. From understanding the intricate workings of your drone to navigating the complexities of airspace regulations, this guide has provided a comprehensive framework for responsible drone piloting. Remember that continuous learning and practice are key to honing your skills and expanding your aerial capabilities.
So, take to the skies, capture stunning visuals, and always prioritize safety.
Understanding drone operation involves several key steps, from pre-flight checks to mastering the controls. Learning how to navigate airspace regulations is also crucial. For a comprehensive guide covering all aspects, including safety protocols and practical flying techniques, consult this excellent resource on how to operate a drone. This will ensure you’re well-prepared before your first flight, enabling safe and responsible drone operation.
FAQ Overview
What is the best drone for beginners?
Successfully piloting a drone involves understanding its controls and mastering basic flight maneuvers. Learning to navigate safely and effectively is crucial, and a great resource for this is the comprehensive guide on how to operate a drone , which covers everything from pre-flight checks to advanced techniques. Understanding these fundamentals ensures responsible and enjoyable drone operation.
Several user-friendly drones are excellent for beginners, often featuring GPS stabilization and automated flight modes. Research models with positive reviews and consider factors like budget and desired features.
How often should I calibrate my drone’s compass?
Compass calibration is crucial for accurate flight. It’s recommended to calibrate before each flight, especially if you’ve moved to a new location or experienced any significant impacts.
What should I do if I lose signal with my drone?
Most drones have a return-to-home (RTH) function. Activate this immediately. If it fails, visually locate your drone and attempt to regain control. If unsuccessful, report the incident to the relevant authorities.
How long does a drone battery typically last?
Drone battery life varies greatly depending on the model, usage (e.g., hovering vs. aggressive maneuvers), and weather conditions. Check your drone’s specifications for estimated flight times.
