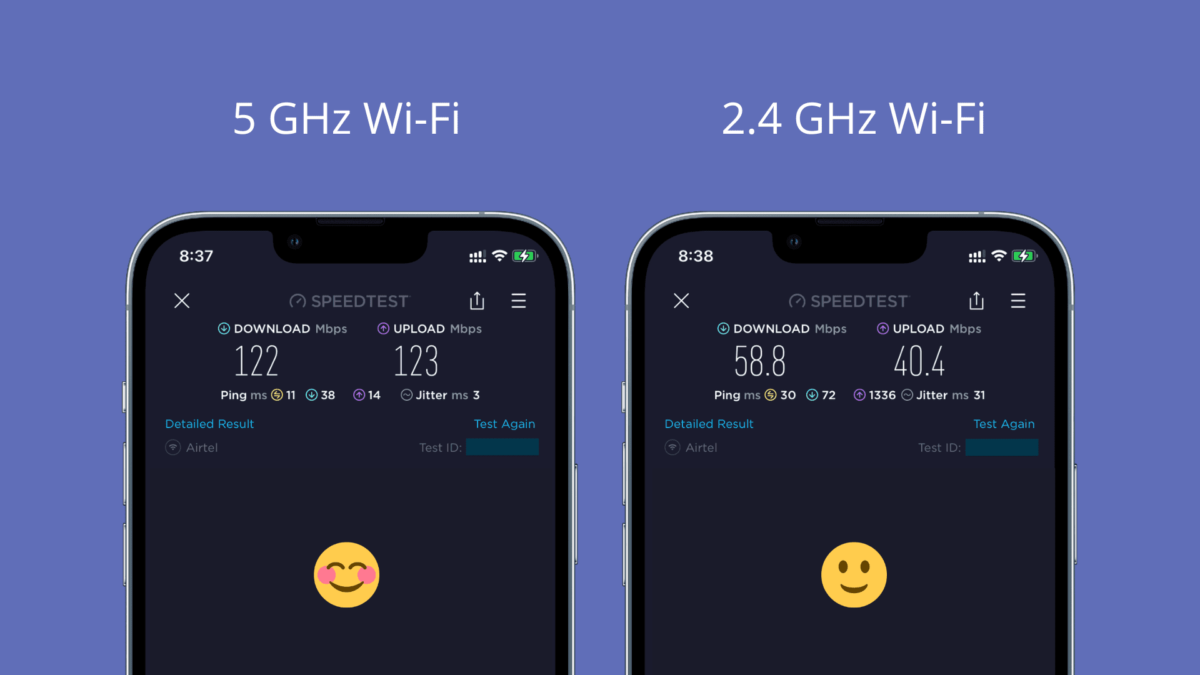
How to check your WiFi GHz on iPhone? It’s easier than you think! Understanding whether you’re connected to the faster 5 GHz band or the more reliable 2.4 GHz band can significantly impact your internet speed and connection stability. This guide will walk you through the simple steps to check your iPhone’s current WiFi frequency, explaining the differences between the two bands and helping you troubleshoot any connection issues.
Okay, so you wanna know your iPhone’s WiFi GHz? It’s usually in your Wi-Fi settings. But hey, while you’re fiddling with settings, check out this cool project, the reality ai lab , for some seriously interesting tech. Then, once you’ve had a look, hop back to your iPhone settings and you should easily find the GHz info you’re after – usually it’s listed right there next to your network name.
We’ll cover everything from finding the settings on your iPhone to understanding what those numbers actually mean.
This guide will break down the process into easy-to-follow steps, showing you exactly where to find the necessary information within your iPhone’s settings. We’ll also cover the pros and cons of each frequency band, helping you understand why choosing the right one is important for optimal internet performance. Whether you’re experiencing slow speeds or just curious about your connection, this guide has you covered.
Understanding WiFi Frequencies on Your iPhone: How To Check Your Wifi Ghz On Iphone
Your iPhone connects to WiFi networks operating on different frequencies, primarily 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz. Understanding the differences between these frequencies is key to optimizing your internet experience. This section will explain the distinctions, advantages, and disadvantages of each, and guide you through identifying your current WiFi frequency.
2.4 GHz and 5 GHz WiFi Networks: A Comparison, How to check your wifi ghz on iphone
The key difference lies in the frequency itself: 2.4 GHz uses a lower frequency, while 5 GHz uses a higher frequency. This difference impacts several aspects of your WiFi connection.
Advantages and Disadvantages of 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz
Here’s a breakdown of the pros and cons of each frequency band:
| Feature | 2.4 GHz | 5 GHz |
|---|---|---|
| Speed | Slower speeds | Faster speeds |
| Range | Longer range, better penetration of walls | Shorter range, weaker penetration of walls |
| Device Compatibility | Wide device compatibility (older devices included) | Limited device compatibility (mostly newer devices) |
| Interference | More susceptible to interference from other devices (microwaves, Bluetooth) | Less susceptible to interference |
Identifying Your WiFi Network’s Frequency
- Go to Settings on your iPhone.
- Tap Wi-Fi.
- Locate the name of your connected WiFi network. You won’t see the frequency directly listed here on most iPhones. You’ll need to check your router’s settings for definitive information.
- (Optional) Access your router’s settings (usually via a web browser) by typing your router’s IP address into the address bar. Consult your router’s manual for instructions on accessing its settings page and finding the frequency of each WiFi band.
Locating WiFi Network Information on Your iPhone
Your iPhone provides several ways to access detailed information about your connected WiFi network, including the SSID, security type, and signal strength. This information is crucial for troubleshooting connection issues.
Accessing WiFi Network Details
The primary method for accessing your WiFi network details is through the iPhone’s Settings app.
Want to know if you’re using the 2.4GHz or 5GHz band on your iPhone’s Wi-Fi? It’s surprisingly easy! Finding out which band you’re connected to helps with troubleshooting slow speeds. To check, you’ll need to dive into your iPhone’s settings; for a step-by-step guide, check out this helpful article: how to check your wifi ghz on iphone.
Once you know your GHz, you can optimize your internet connection for better performance.
Viewing SSID and Security Type
The SSID (Service Set Identifier) is the name of your WiFi network. The security type indicates the level of encryption used (e.g., WPA2, WPA3). This information is displayed in the WiFi settings menu after connecting to a network.
Determining Signal Strength
Your iPhone visually represents the signal strength using a series of bars or dots. A full set of bars indicates a strong signal, while fewer bars indicate a weaker signal. This is usually displayed next to your connected network’s name in the WiFi settings.
Visual Representation of WiFi Settings Location
Imagine the iPhone’s home screen. Swipe up from the bottom to access the app library (or find the Settings app icon). Tap the grey Settings icon (it resembles a gear). Then, tap “Wi-Fi”. The connected network information, including the SSID, security type and signal strength indicator, is displayed here.
Interpreting WiFi Network Information
Understanding the indicators of a weak WiFi signal and their potential causes is essential for effective troubleshooting. This section provides guidance on identifying and resolving slow or unstable connections.
Indicators of a Weak WiFi Signal
A weak WiFi signal is typically indicated by a low number of signal bars in the WiFi settings, slow loading times for websites and apps, and intermittent connectivity drops.
Causes of Weak or Unstable Connections

Several factors can contribute to weak or unstable connections, including physical distance from the router, obstacles between the iPhone and router (walls, furniture), interference from other electronic devices, and network congestion.
Troubleshooting a Slow WiFi Connection
- Check your distance from the router: Move closer to the router to see if the signal improves.
- Identify and remove obstacles: Try to minimize obstacles between your iPhone and the router.
- Restart your iPhone and router: A simple restart can often resolve temporary glitches.
- Check for interference: Move your router away from other electronic devices that might be causing interference.
- Check for network congestion: If many devices are connected to your WiFi network, consider upgrading your router or using a WiFi extender.
Advanced WiFi Settings and Troubleshooting
This section delves into more advanced WiFi settings and troubleshooting techniques, including switching between WiFi bands, managing WiFi channels, and understanding WiFi protocols.
Switching Between 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz Networks
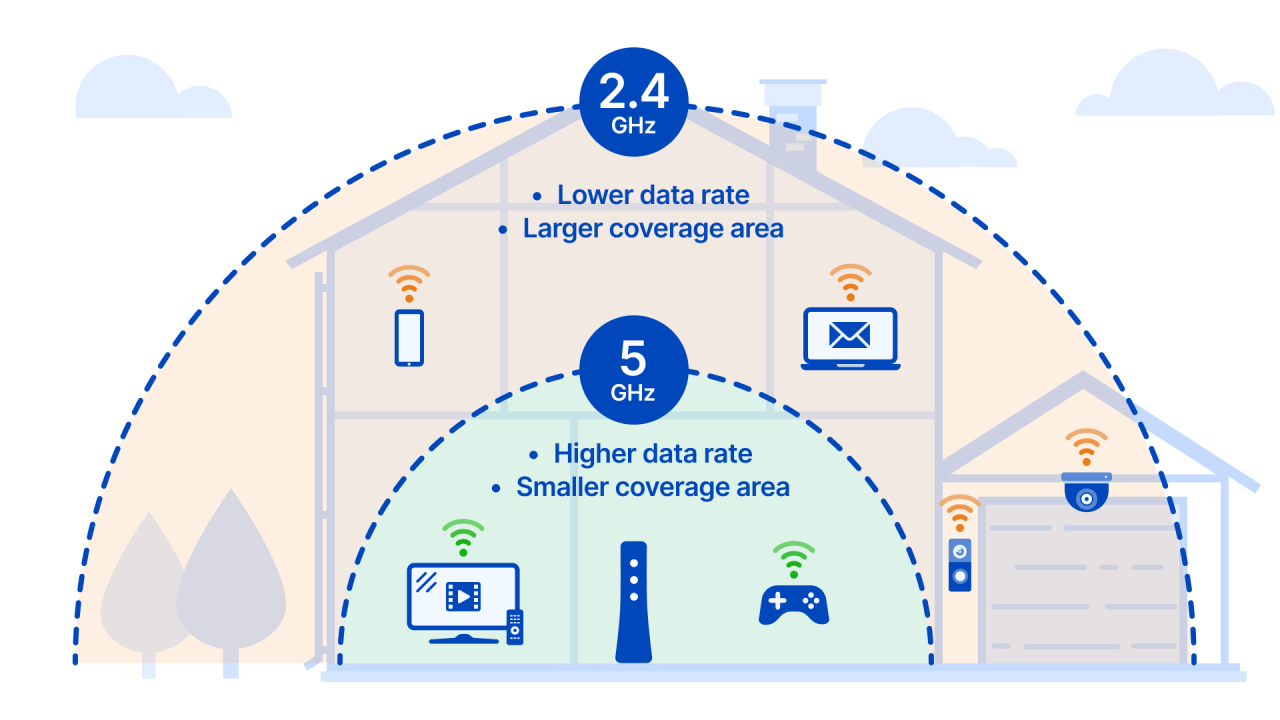
If your router supports both 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz networks, you can usually select the desired band directly within your router’s settings. Your iPhone will then connect to the selected band. However, remember that your device must support the chosen frequency.
WiFi Channel Selection
WiFi channels are like lanes on a highway. Choosing a less congested channel can improve network performance. This is typically configured within your router’s settings.
Forgetting and Reconnecting to a WiFi Network
Sometimes, forgetting and reconnecting to a WiFi network can resolve connection issues. This process involves removing the network from your iPhone’s settings and then re-entering the network password.
Comparison of WiFi Protocols
Different WiFi protocols (like 802.11ac and 802.11ax/Wi-Fi 6) offer varying speeds and capabilities. Newer protocols generally offer faster speeds and improved efficiency. Check your router and device specifications to determine the supported protocols.
Visual Aids and Explanations
Visual cues and descriptions help in understanding WiFi signal strength and its impact on performance.
Figuring out your iPhone’s Wi-Fi GHz is pretty straightforward, usually found in your Wi-Fi settings. But if you’re curious about your device’s overall hardware specs, including how it handles different Wi-Fi frequencies, checking out a program like cpu z can be helpful. This gives you a broader picture, though remember to focus on the settings app on your iPhone for precise Wi-Fi GHz details.
Visual Representation of WiFi Signal Strength
Imagine a series of five filled-in bars representing the signal strength. Five bars indicate an excellent signal, four bars a good signal, three bars a fair signal, two bars a weak signal, and one bar a very weak signal. No bars indicate no signal.
Correlation Between Visual Representation and Network Performance
The number of bars directly correlates with the strength of the WiFi signal. A higher number of bars indicates a stronger signal and better performance, while fewer bars indicate a weaker signal and potentially slower speeds or dropped connections. For example, streaming video might buffer frequently with only one or two bars.
Scenario for Switching Between 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz
If you’re experiencing slow speeds while using a device that supports 5 GHz, switching to the 5 GHz band could significantly improve your speeds, provided the signal strength is adequate. However, if you’re far from the router or have many obstacles, the 2.4 GHz band might offer better connectivity despite lower speeds.
Factors Affecting WiFi Signal Strength
Several factors affect WiFi signal strength. Distance from the router is a major factor, as signal strength weakens with distance. Obstacles like walls and furniture can significantly attenuate the signal. Interference from other electronic devices operating on similar frequencies can also degrade performance. Finally, network congestion, with many devices using the same network, can lead to reduced performance for all users.
Closure
Mastering your iPhone’s WiFi settings is key to a smooth and speedy internet experience. By understanding the difference between 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz networks, and knowing how to check which one you’re connected to, you can troubleshoot problems and optimize your connection. Remember to consider factors like distance from your router and potential interference when evaluating your WiFi performance.
Now you’re equipped to take control of your wireless connection and enjoy faster, more reliable internet on your iPhone!
Essential Questionnaire
What does GHz mean in relation to WiFi?
GHz stands for Gigahertz, representing the frequency of the WiFi signal. Higher GHz generally means faster speeds but shorter range.
Why is my WiFi speed slower on 5 GHz?
Several factors can cause slow speeds on 5 GHz, including distance from the router, interference from other devices, and the router’s capabilities. Obstacles like walls can also significantly reduce the signal strength.
My router only shows one WiFi network. Can I still check the GHz?
If your router doesn’t broadcast separate 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz networks, you’ll need to check your router’s settings directly to determine which frequency it’s using.
Can I force my iPhone to connect to a specific GHz band?
Not directly on the iPhone itself. You’ll usually need to configure your router to create separate networks for each band (2.4 GHz and 5 GHz) and then connect to the desired one.